Dorset culture

Remains of a Dorset stone longhouse in Cambridge Bay, Nunavut

Carving of a polar bear
The Dorset was a Paleo-Eskimo culture, lasting from 500 BC to between 1000 and 1500 AD, that followed the Pre-Dorset and preceded the Inuit in the Arctic of North America. It is named after Cape Dorset in Nunavut, Canada where the first evidence of its existence was found. The culture has been defined as having four phases due to the distinct differences in the technologies relating to hunting and tool making. Artifacts include distinctive triangular end-blades, soapstone lamps, and burins.
The Dorset were first identified as a separate culture in 1925. The Dorset appear to have been extinct by 1500 at the latest and perhaps as early as 1000. The Thule people, who began migrating east from Alaska in the 11th century, ended up spreading through the lands previously inhabited by the Dorset. There is no strong evidence that the Inuit and Dorset ever met. Modern genetic studies show the Dorset population were distinct from later groups and that "[t]here was virtually no evidence of genetic or cultural interaction between the Dorset and the Thule peoples."[1]
Inuit legends recount them encountering people they called the Tuniit (singular Tuniq) or Sivullirmiut "First Inhabitants". According to legend, the First Inhabitants were giants, taller and stronger than the Inuit but afraid to interact and "easily put to flight."[2] There is also a theory of contact and trade between the Dorset and the Norse.
Contents
1 Discovery
2 History
2.1 Origins
2.2 Historical and cultural periods
3 Technology
4 Interaction with the Inuit
4.1 The Sadlermiut
5 Dorset in culture
6 See also
7 Bibliography
8 References
9 External links
Discovery
In 1925 anthropologist Diamond Jenness received some odd artifacts from Cape Dorset. As they were quite different from those of the Inuit, he speculated that they were indicative of an ancient, preceding culture. Jenness named the culture "Dorset" after the location of the find. These artifacts showed a consistent and distinct cultural pattern that included sophisticated art distinct from that of the Inuit. For example, the carvings featured uniquely large hairstyles for women, and figures of both sexes wearing hoodless parkas with large, tall collars. Much research since then has revealed many details of the Dorset people and their culture.
History
Origins
The origins of the Dorset people are not well understood. They may have developed from the previous cultures of Pre-Dorset, Saqqaq or (less likely) Independence I. There are, however, problems with this theory: these earlier cultures had bow and arrow technology which the Dorsets lacked. Possibly due to a shift from terrestrial to aquatic hunting, the bow and arrow became lost to the Dorset. Another piece of technology that is missing from the Dorset are drills: there are no drill holes in Dorset artifacts. Instead, the Dorset gouged lenticular holes. For example, bone needles are common in Dorset sites, but they have long and narrow holes that have been painstakingly carved or gouged. Both the Pre-Dorset and Thule (Inuit) had drills.
Historical and cultural periods
See also archaeologist Patricia Sutherland's theory of contact and trade between the Dorset and the Norse in Nanook, Baffin Island
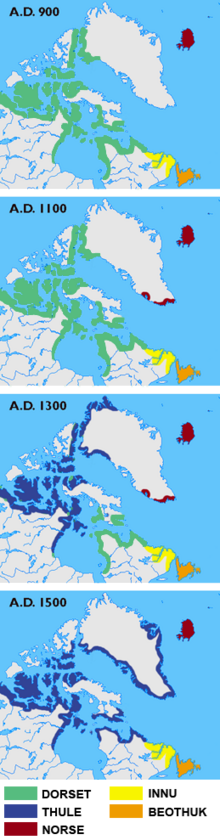
The decline of the Dorset Culture people - 900 to 1500 CE
Dorset culture and history is divided into four periods: the Early (500-1 BC), Middle (AD 1-500), and Late phases (AD 500-1000), as well perhaps as a Terminal phase (from c. AD 1000). The Terminal phase, if it existed, would likely be closely related to the onset of the Medieval Warm Period, which started to warm the Arctic considerably around AD 950. With the warmer climates, the sea ice became less predictable and was isolated from the High Arctic.
The Dorset were highly adapted to living in a very cold climate, and much of their food is thought to have been from hunting sea mammals that breathe through holes in the ice. The massive decline in sea-ice which the Medieval Warm Period produced would have strongly affected the Dorset. They could have followed the ice north. Most of the evidence suggests that they disappeared some time between AD 1000 and 1500. Scientists have suggested that they disappeared because they were unable to adapt to climate change[3] or that they were vulnerable to newly introduced disease.[4]
Technology
The Dorset adaptation was different from that of the whaling-based Thule Inuit. Unlike the Inuit, they rarely hunted land animals, such as polar bears and caribou. They did not use bows or arrows. Instead, they seem to have relied on seals and other sea mammals that they apparently hunted from holes in the ice. Their clothing must have been adapted to the extreme conditions.
Triangular end-blades, soapstone, and burins are diagnostic of the Dorset. The end-blades were hafted onto harpoon heads. They primarily used the harpoons to hunt seal, but also hunted larger sea mammals such as walrus and narwhals. They made kudlik lamps from soapstone and filled them with seal oil. Burins were a type of stone flake with a chisel-like edge. They were probably either used for engraving or for carving wood or bone. The burins were also used by Pre-Dorset groups and had distinctive mitten shape.
The Dorset were highly skilled at making refined miniature carvings, and striking masks. Both indicate an active shamanistic tradition. The Dorset culture was remarkably homogeneous across the Canadian Arctic, but there were some important variations which have been noted in both Greenland and Newfoundland/Labrador regions.[citation needed]
Interaction with the Inuit
There appears to be no genetic connection between the Dorset and the Thule who replaced them.[5] Archaeological and legendary evidence is often thought to support some cultural contact, but this has been questioned.[6] The Thule, for instance, engaged in seal-hole hunting, a method which requires several steps and includes the use of dogs. The Thule apparently did not use this technique in the time they had previously spent in Alaska. Settlement pattern data has been used to claim that the Dorset also extensively used a breathing-hole sealing technique and perhaps they would have taught this to the Inuit. But this has been questioned on the grounds that there is no evidence that the Dorset had dogs.[6]
Some elders describe peace with an ancient group of people, while others describe conflict.[7]
The Sadlermiut
The Sadlermiut were a people living in near isolation mainly on and around Coats Island, Walrus Island, and Southampton Island in Hudson Bay up until 1902–03. Encounters with Europeans and exposure to infectious disease caused the deaths of the last members of the Sadlermiut.
Scholars had believed the Sadlermiut were the last remnants of the Dorset culture, as they had a culture and dialect distinct from the mainland Inuit. Supporting this a 2002 mitochondrial DNA research showed that the Sadlermiut bore a mitochrondrial relationship to both the Dorset and Thule peoples, perhaps suggesting local admixture.[8]
However a subsequent 2012 genetic analysis showed no genetic link between the Sadlermiut and the Dorset.[9]
Dorset in culture
Canadian poet Al Purdy wrote a poem entitled "Lament for the Dorsets" which starts "Animal bones and some mossy tent rings... all that remains of Dorset giants, who drove the Vikings back to their longships..." This poem laments the loss of their culture and describes them and their end.
See also
- Qajartalik
- Saqqaq culture
- Thule people
Bibliography
- Michael Fortescue, Steven Jacobson & Lawrence Kaplan (1994): Comparative Eskimo Dictionary; with Aleut Cognates (Alaska Native Language Center Research Paper 9); .mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
ISBN 1-55500-051-7
- Robert McGhee (2005): The Last Imaginary Place: A Human History of the Arctic World;
ISBN 0-19-518368-1
- Robert McGhee (2001): Ancient People of the Arctic
Plummet Patrick, Lebel Serge (1997). "Dorset Tip Fluting: A Second 'American' Invention". Arctic Anthropology. 34 (2): 132–162.
Renouf M.A.P. (1999). "Prehistory of Newfoundland Hunter-Gatherers: Extinctions or Adaptations?". World Archaeology. 30 (3): 403–420. doi:10.1080/00438243.1999.9980420.
References
^ "Dorset DNA: Genes Trace the Tale of the Arctic's Long-Gone 'Hobbits' - NBC News". NBC News.
^ "When science meets aboriginal oral history". Toronto Star.
^ "New Study Offers Clues to Swift Arctic Extinction". New York Times.
^ "The strange history of the North American Arctic". Science AAAS.
^ Maanasa Raghavan; Eske Willerslev; et al. (August 29, 2014). "The genetic prehistory of the New World Arctic". Science. 345 (6200): 1020. doi:10.1126/science.1255832. PMID 25170159. Retrieved 2015-08-08.
^ ab Robert W. Park (1993). "The Dorset-Thule succession in Arctic North America: Assessing claims for culture contact". American Antiquity=volume=58 (2). pp. 203–234.
^ "Inuit stories of the Tuniit backed up by science". Northern News Services.
^ "Arctic Studies Center Newsletter page 34" (PDF). National Museum of Natural History. Smithsonian Institution. June 2002. Retrieved 2008-10-13.
^ Robert W. Park (August 29, 2014). "Stories of Arctic colonization". Science. 345 (6200): 1004–05. doi:10.1126/science.1258607. PMID 25170138. Retrieved 2015-08-08.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Dorset culture. |
"Dorset Culture in Nunavik", Avataq
"In the bones of the world", Nuntsiaq News
"Sadlermiut", Canadian Encyclopedia
"Dorset Paleoeskimo Culture", Canada.ca.